Bandwidth refers to the maximum rate at which data can be transferred over a network or communication channel in a given amount of time. It’s typically measured in bits per second (bps)
Multiplexing
Multiplexing is a technique that combines multiple signals—like data, voice, or video—into a single transmission medium to make efficient use of bandwidth
-
Frequency-Division Multiplexing (FDM)
- Type: Analog
- Description: This technique divides the available frequency bandwidth into separate channels, each allocated a specific frequency range. Multiple signals are transmitted simultaneously, each using its own frequency band, without interfering with others. For example, radio and television broadcasting often use FDM.
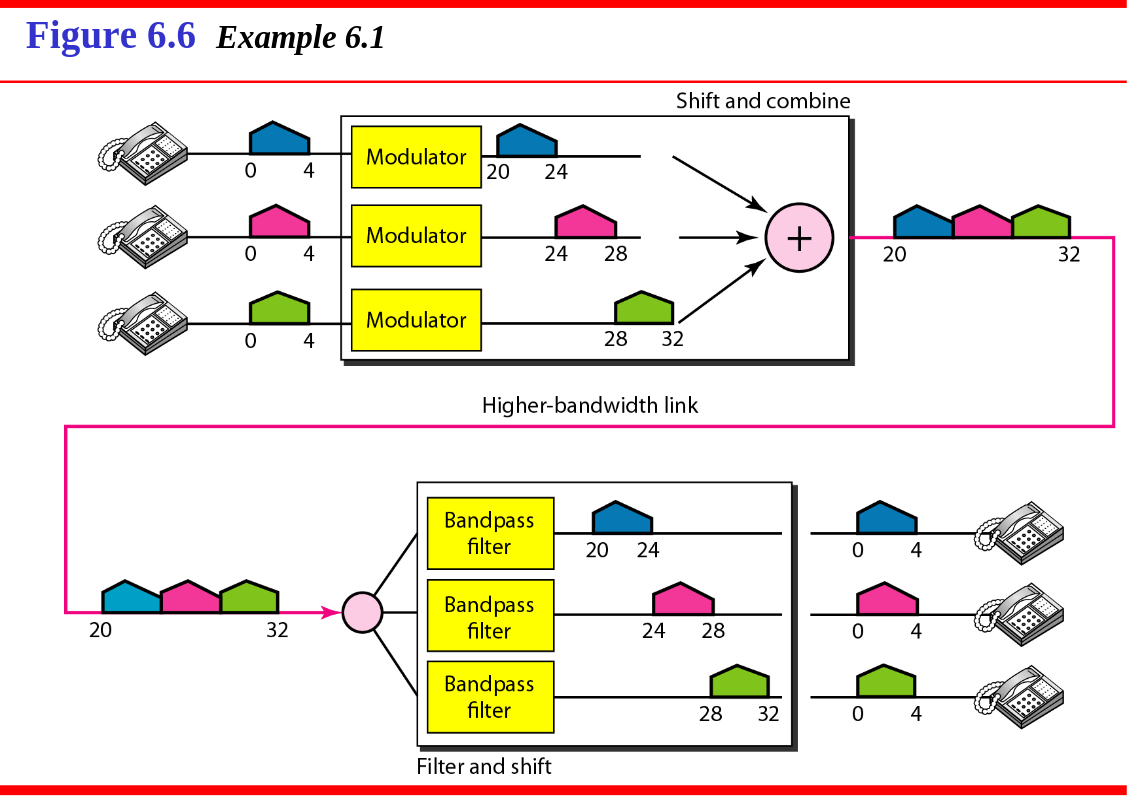
-
Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM)
- Type: Analog
- Description: Commonly used in fiber-optic communication, WDM splits the light spectrum into different wavelength bands (colors of light). Each signal is carried on a different wavelength, allowing multiple data streams to travel over the same optical fiber simultaneously. It’s widely used in high-capacity networks like the internet backbone.
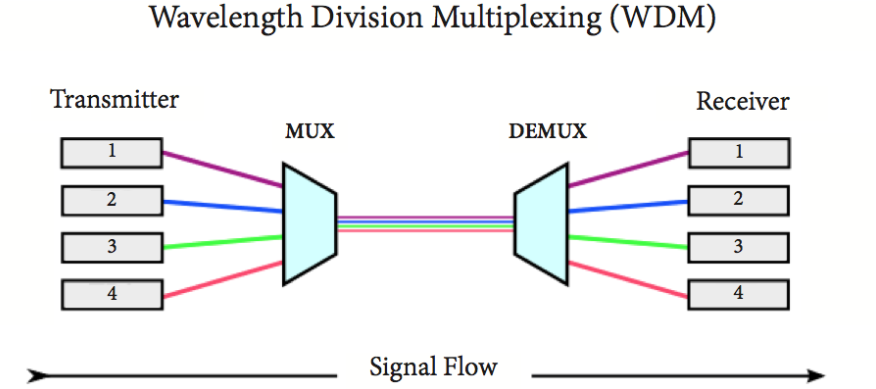
- Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- Type: Digital
- Description: This method divides the transmission time into slots, and each signal gets a specific time slot to transmit its data. The signals are sent in rapid succession, taking turns to use the entire bandwidth. TDM is common in digital telephone systems and modern network protocols like T1 lines.