Economics is the study of choices and not about the money.
Types of scarcity
-
Scarcity of land
-
Scarcity of labor
-
Scarcity of Capital
-
Scarcity of Entrepreneurship
According to Kautilya, “The intention of a human being is ‘arth’ (wealth); the piece of land which has human settlement is ‘arth’(wealth) and thus the science expanding the purpose and utility of wealth creation on earch is called Economics”
Economics definitions
- Economics is the study of nature and causes of wealth of nations - Adam Smith
- Economics is the study of mankind in the ordinary business of life implies that in every people usually seek material well-being - Alfred Marshall
- Economics is the science which studies human behaviour as a relationship between ends and scarce means which have alternative uses.
Modern definition
Economics is the study of choice making individuals, institutions, societies, nations and globe under conditions of scarcity and surplus toward maximizing benefits satifying thier unlimited needs at present and future.
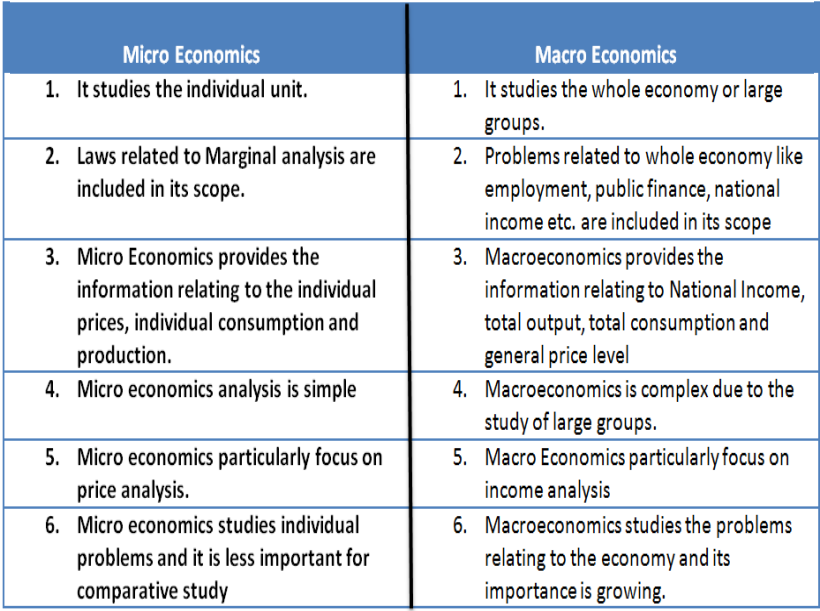
Types of Economics
- Microeconomics
- branch that examines the behaviour of individual decision making units.
- study of behaviour of individual households
- per capita income.
- Macroeconomics
- branch of economics that examines the behaviour of economics aggregates - income, output, employment.
- study of economics as a whole
- GDP, govt. spending, trade deficity
Science, Engineering and technology and economics development
- Science - it is a systematic body of knowledge based on facts, having cause and effect relationship, can be experimented to produce generalized true principles.
- Engineering - it can be defined as application of scientific and mathematical principles used for practical purposes like design, manufacture, and operation or efficient economical structures, machines, processes, and systems.
- Technology - y can be broadly defined as the entities, both material and immaterial, created by the application of mental and physical effort inorder to achieve some value.
- Economic Development - is the growth of the standard of living of a nations people from a low-income (poor) economy to a high-income (rich) economy or low-income national economies are transformed into modern industrial economies. When the local quality of life is improved, there is more economic development.
Economic Development
Economic Development = Economic Growth + Change
Economic development implies inclusive growth i.e. Growth with development in terms of changes in the way the organisation / nation functions
Significance of Economics
- Important for individual
- important for business firms
- important for nations
Why study Economics
- To understand the world better
- To gain self confidence
- To achieve social change
- Deciding which manufacture to buy good from.
- Deciding the price and the quantity of commodity to be produced.
- Deciding on the level of inventory a firm will maintain of product or raw material.
- Making employment decisions.
- Making decisions regarding further business investment.
Key concepts of economics
- Consumer - An individual who buys various good and services to satisfy his or her wants.
- Consumption - An act of consumer which is concerned with the use of various goods and services to satisfy wants.
- Producer - An individual who is involved with the activity of producing goods as a farmer or a manufacturer.
- Production - An act of a producer to produce various goods and services, which is concerned with creating utility to satisfy consumer wants.
- Utility - The capacity of a commodity to satisfy human wants.
- Exchange - An act of selling and buying goods and services.
- Factors of production - The term used for resources of society which are used in the process of t production like land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship.
- Factor incomes - incomes accruing to the factors of productions in the term of rent, wage, interest and profit.
- Investment - The purchase of goods that are not consumed today but are used in the future to create wealth.
- Savings - Excess of income over the expenditure.
Factors of production
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
- Entrepreneurship
Production possibility curve
It is a graph that compares the production rates of two commodities(guns and butter) that use the same fixed total of factors of production set, the PPF curve shows the max specified production level of one commodity that results given the production level of another.
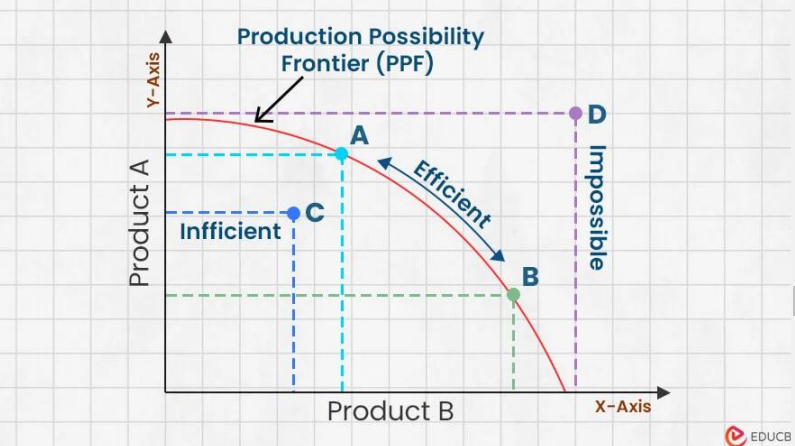
Use of PPC
- Knowledge of economic efficieny
- Choice of techniques of production
- Distribution of the national income
- Opportunity cost analysis
- Economic growth measurement
- Understanding Unemployement and inefficieny
- Understanding Economic Problems
Economics Laws
- These are statements of uniformities which govern human behaviour concerning the utilization of limited resources for attainment of unlimited ends.
- Economics laws are human laws
- Economics laws are hypothetical
- Economic laws are less universal
- Economic laws have poor predictability
- Economic laws can not be subjected to controlled experiment.
Methods of Economics
- Positive
- Normative